Case Study
Prevalence & Overlap
of Cardiac, Renal &
Metabolic Conditions
in US Adults
The Question
CRM conditions are leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the US, with cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and type 2 diabetes (T2D) estimated to account for approximately 1 in every 3 deaths in the contemporary era. These conditions are deeply interconnected, with disease onset in each system often preceded by shared pathophysiology and risk factors.
Owing to unique pathways of comorbidity attainment and recent therapeutic innovations targeting specific forms of CRM overlap, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, individual CRM intersections are increasingly clinically and therapeutically relevant.
Our analysis aimed to estimate the contemporary prevalence and overlap of CVD, CKD, and T2D among US adults, as well as temporal trends from 1999-2020.
The Approach
Nationally representative data of US adults was collected using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 1999-2020. Participants with data available to determine CRM status were included in this analysis. Contemporary estimates were based upon the period from 2016-2020. Temporal trends were assessed through logistical regression across four combined periods: 1999-2002, 2003-2008, 2009-2014, and 2015-2020.
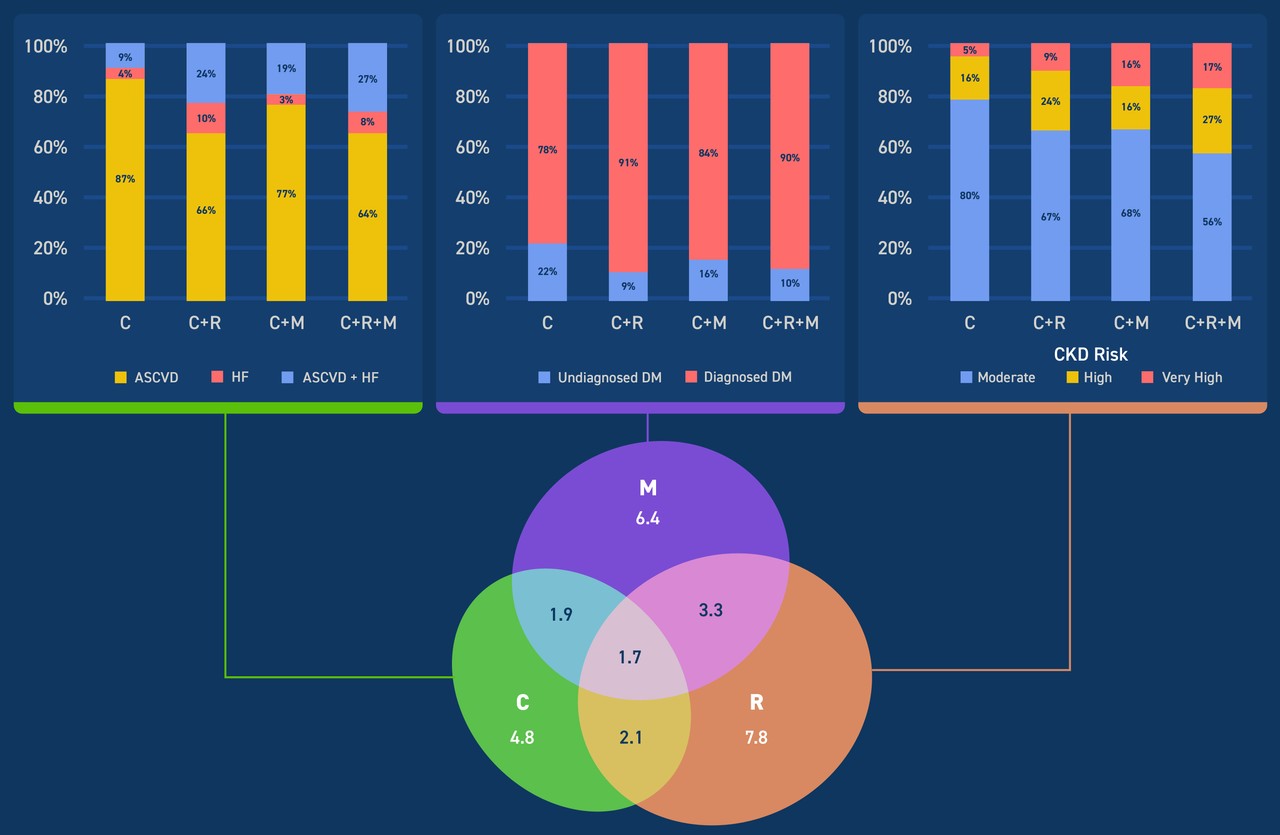
The Results
Contemporary overlap: In 2015-2020, 19.0% of US adults had 1 CRM condition, 7.3% had 2 CRM conditions, and 1.7% had 3 CRM conditions.
Racial and socioeconomic disparities
CRM comorbidity burden was disproportionately high among participants reporting non-Hispanic Black race or ethnicity, unemployment, low socioeconomic status, and no high school degree.
Temporal trends
From 1999 through March 2020, the proportion of US adults with at least 1 CRM condition increased from 21.2% in 1999-2002 to 26.3% in 2015-2020 (P < 0.001 for test of linear trend).
The Long And
Short Of it
Our analysis led to an ongoing research partnership between the client, leading clinical experts, and the Medicus team. Results from the analysis supported value messaging for their new therapy, with results disseminated as a poster presentation (American Society of Nephrology) and manuscript publication in JAMA Cardiology.